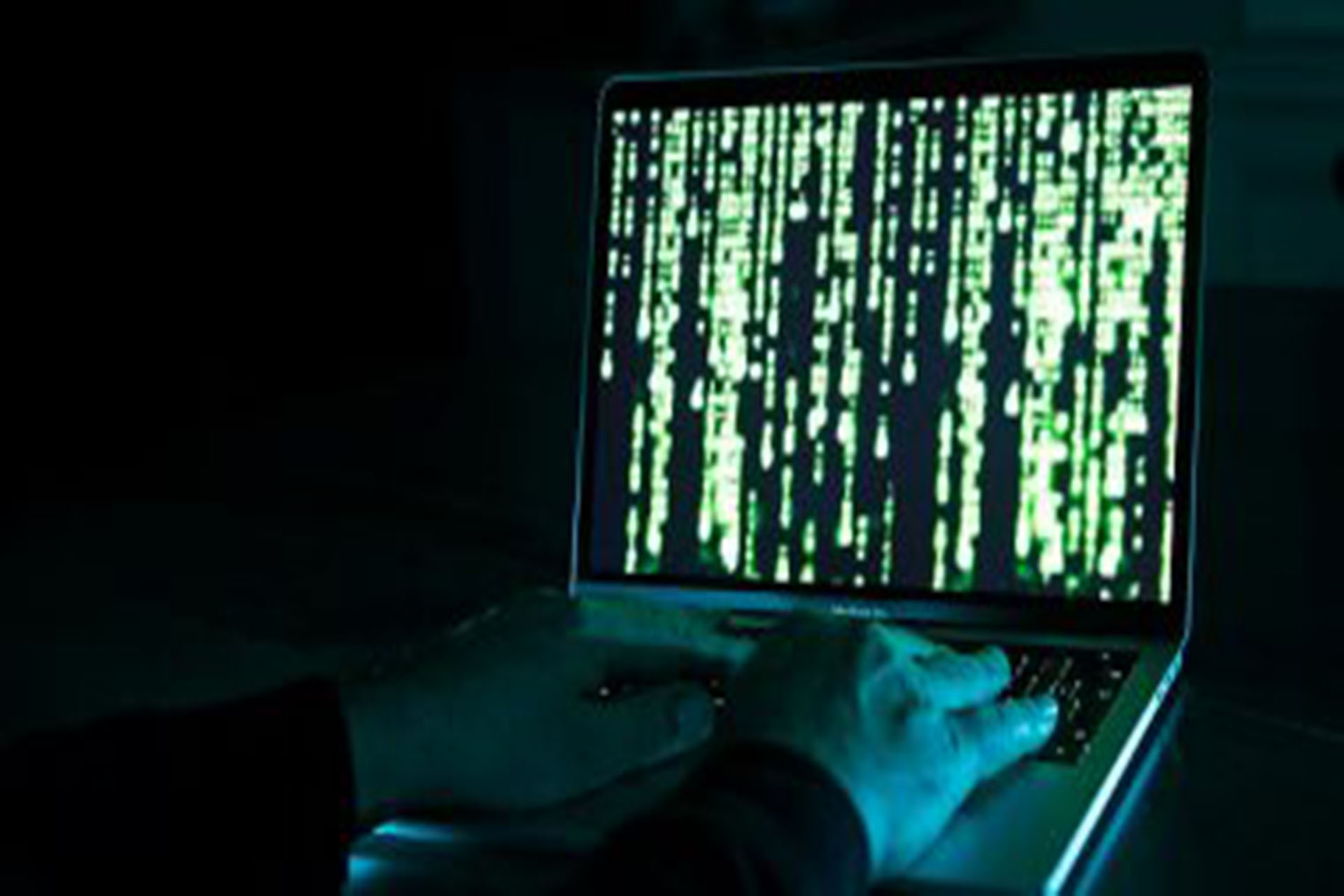
Over the past year, there has been a significant increase in ransomware attacks worldwide, reaching their highest ever peaks. Between June 2022 and June 2023, the United States has experienced the highest number of attacks, accounting for about half of all reported incidents, while India is also among the top 10 most affected countries.
The United States was the most affected, accounting for more than 43% of the 1,900 reported incidents, a 75% jump from previous year’s figures, according to a report by MalwareBytes, in addition to the United States, Germany, France and the United Kingdom also saw an increase in ransom attacks, albeit at a lower frequency.
In the United States, emergency rooms have been closed in many states due to a cyber attack that disrupted hospital computer systems in the United States, and cyberattacks and data breaches are increasingly widespread globally, with universities, schools, hospitals, governments and agencies experiencing security breaches.
In June, Russian hackers targeted private companies and U.S. agencies, including the Department of Energy, and experts reported $450 million in ransomware payments in the first half of 2023, a significant increase from 2022, and France and Germany were both impacted by the growing threat of ransomware.
Germany remains the fourth most targeted country globally and most targeted for non-English speaking countries, on the other hand, France has faced a large number of attacks on its government sector, accounting for 9% of all attacks, and at the same time, India has recorded 63 reported incidents over the past year.
The global ransomware attack witnessed a “serious leap” last year
The report identified 48 distinct ransomware groups that targeted U.S. companies, government entities, and individual consumers within the set timeframe. Health and educational institutions were the most hit, and the report highlights the alarming evolution of the cyberattacks world – the rise of CL0P has been able to exploit the zero-day gaps to increase the severity of their attacks, potentially changing the game for the worse.
Until recently, LockBit was the most prevalent form of “Ransomware-as-a-Service” in the U.S., with an average of 24 monthly attacks over the last 18 months, however, CL0P exceeded this rate twice this year, in March and June, due to the use of the Day Zero gaps in GoAnywhere MFT and MOVEit Transfer.
This change in tactics can have serious consequences for the future of ransomware strategies, if groups adopt more CL0P’s Zero Day exploit technologies, there may be a shift towards vulnerability-focused attacks, which could lead to increased victims. This trend is similar to the adoption of a “dual extortion” tactic in 2019.